Ask anyone (except for a biochemist), about caffeine consumption, how our bodies react to caffeine, and the amount of caffeine extracted from coffee beans, and you’ll have a pile of incorrect answers that range from mother-in-law “facts” to Google urban legends. We hope to share some valid insights and information regarding caffeine and coffee and how it works since a lot of people ask about the subject matter. So that’s exactly what we will address in this post: what caffeine is, how it works, and how much of it your cup of coffee or espresso contains.
What is Caffeine and How Does it Work?
You know that state of bliss you enter after your first shot of espresso or cup of drip coffee? Well, you can thank four unique compounds for that joyful caffeinated glow you get after downing a delicious cup of coffee.
Adenosine

Caffeine blocks the Adenosine receptors in your brain, which, in turn, helps you become more alert. Adenosine is a naturally occurring chemical that your body produces to help you sleep. Once produced, it binds to receptors in your body to complete a chemical reaction that slows your body down.
Adenosine also lowers your blood pressure and dilates your blood vessels to increase oxygenation for a good night’s sleep. Caffeine shares a similar chemical structure, so it can also bind to your receptors and reduce, or possibly even negate the effect of Adenosine. With fewer available receptors, neural activity increases, which makes you feel more alert. This is one of the primary reasons why it’s difficult to sleep after consuming caffeine.
Adrenaline

All of the extra brain activity brought upon by Adenosine blocking your receptors causes your body to produce Adrenaline. Adrenaline is a hormone that your adrenal glands release. Its primary action is to prepare your body for “fight or flight” mode. While your brain starts to speed up, your body believes that it is in a threatening situation, so it starts to produce low doses of Adrenaline. Adrenaline provides you with a small boost of energy. You know that shaky feeling you get after having one too many cups of coffee? Well, that’s a sign that your body is reacting to the added Adrenaline the same way it would in a stressful situation. This is very similar to what your body experiences when it enters “fight or flight” mode.
Dopamine
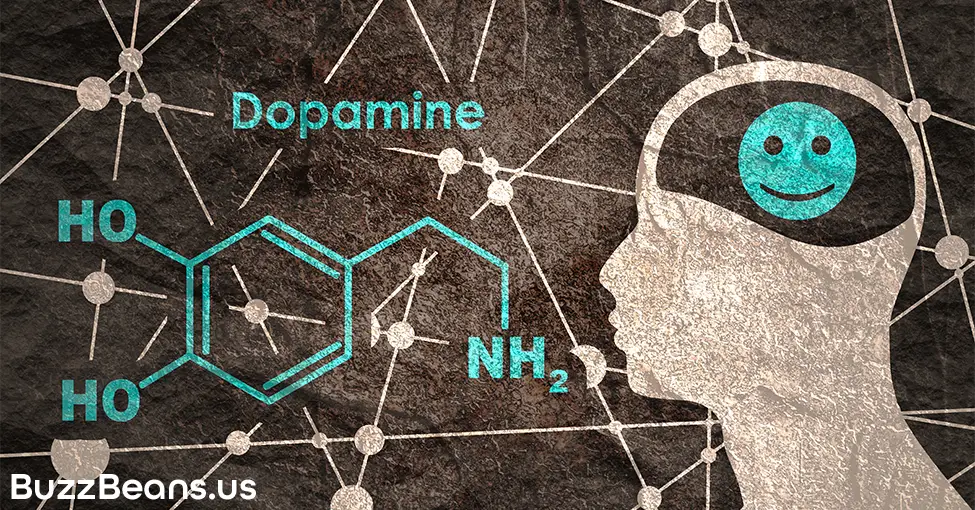
Similar to the dash of sweetness that balances out the bitterness in a shot of espresso, caffeine helps balance adrenal stress by reducing dopamine reabsorption. Dopamine does a lot within the human brain. However, the hallmark characteristic of dopamine is the feeling of euphoria that it creates. When you consume caffeine, it hinders your ability to break down Dopamine. This means that you’ll have a surplus of the feel-good compound in your system for longer than normal.
Early research suggested that caffeine actually produced Dopamine in a similar way as anti-depressants and illegal drugs like cocaine. However, we now know that caffeine doesn’t produce dopamine. Instead, caffeine blocks the reabsorption of dopamine, which, in turn, makes the euphoric feeling last longer. As most caffeine consumers know, this feeling is rather addictive.
Theophylline
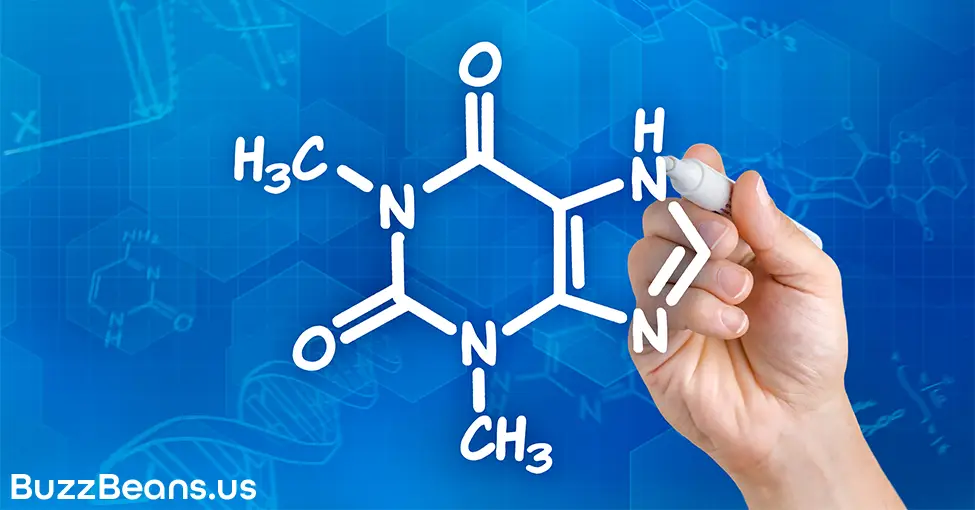
Theophylline is a bronchodilator. It relaxes your blood vessels and smooth muscles, which increases your ability to breathe. While caffeine has no direct impact on Theophylline, it looks similar to the compound from a chemical perspective. It looks so similar that it tricks the body into thinking that it is one. This is why athletes of all sorts enjoy caffeine so much – it increases lung function. This soothing of the smooth muscles is also known to cause a well-documented effect in humans – bowel movements. While there is no scientific evidence to support this theory, the causal evidence is overwhelming. It is worth noting that Theophylline is not a diuretic – science debunked this myth in 2015.
How Much Caffeine Is There In My Coffee?
Like so many things in life, the short answer is – it depends. If we want to find out how much caffeine is in your drip coffee or espresso, we’ll need to do some digging and some math.
Caffeine makes up around 1% of the total composition of roasted arabica coffee. Despite what you may have heard, this is true regardless of the roast level. Caffeine can handle the high temperatures required for roasting coffee without breaking down or cooking off. In terms of quantity, there are roughly 100 milligrams of caffeine for every 10 grams of coffee if we follow the 1% rate.

However, most of us don’t consume straight-roasted coffee. Instead, we drink a solution of water and dissolved organic compounds – aka coffee. This means that it is unlikely that we extract all of the available caffeine in our standard ground coffee. In most cases, the average coffee drinker extracts 80-90% of the available caffeine during the brewing process. So, in order to find out how much caffeine we consume, we simply multiply the amount of ground coffee (grams) by 8.
The amount of caffeine will vary depending on the type of filter you use. On one hand, you have paper filters that prevent small particles of coffee from draining into your cup. On the other hand, metal and cloth filters used for espresso and French press brews allow for coffee sediment to pass into your morning cup of wake-me-up juice. These small pieces of coffee still have the leftover caffeine and will ultimately increase the caffeine content slightly.
How Long Do the Effects of Caffeine Last?
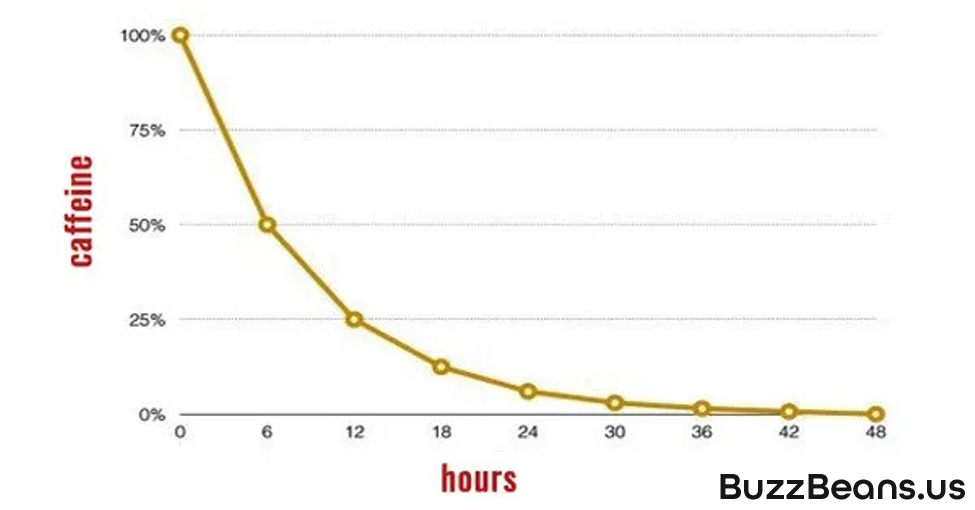
Most will find this relatively shocking, but 99% of ingested caffeine passes into your bloodstream within 45 minutes of consumption. Furthermore, the half-life of caffeine, or how quickly 50% of the caffeine you consume metabolizes in your body, is in the neighborhood of 5 hours.
Let’s break this concept down with an example! If you consume 300mg of caffeine at 7:00 in the morning, roughly 150mg of the initial caffeine you consumed will still be active in your body at noon. As with most chemical compounds, this trend occurs in a downward curve. The “crash” you experience when the ingested caffeine is fully metabolized is the result of the reactions we discussed earlier reversing. This is especially true of the Adenosine receptors becoming available again.
Why Does Coffee Contain Caffeine?
Caffeine occurs naturally and is found in a variety of plants, primarily coffee, tea, and chocolate. Per evolutionary biologists, caffeine offers a number of key benefits to its host plant that help it survive and thrive.
This may leave your jaw on the floor, but caffeine is an effective pesticide. While it takes 10 grams of pure caffeine to trigger a human overdose, it takes just a dollop to kill your average insect. Furthermore, caffeine helps coffee plants develop an advantage over other plants growing nearby. Extra caffeine ends up in the soil as coffee plants drop their leaves and/or die. This makes it harder for competing plants to take root and steal valuable resources.
Lastly, caffeine isn’t only a deterrent. The nectar of coffee plants features a small amount of caffeine. Insects that feed off the nectar get a nice buzz and eventually develop a casual addiction to said buzz.
If you’re hungry for more juicy health benefits associated with coffee, you should check out this article.
So now that you know all about caffeine and its effects, it’s time to enjoy a cup of joe! At Buzz Beans, we love sourcing the best coffee beans from around the world and bringing them right to your doorstep. Get that magical caffeine glow and snag a bag of our beans today!




